Name
scale()
Description
Increases or decreases the size of a shape by expanding and contracting
vertices. Objects always scale from their relative origin to the coordinate
system. Scale values are specified as decimal percentages. For example, the
function call scale(2.0) increases the dimension of a shape by
200%.
Transformations apply to everything that happens after and subsequent calls
to the function multiply the effect. For example, calling scale(2.0)
and then scale(1.5) is the same as scale(3.0). If
scale() is called within draw(), the transformation is reset
when the loop begins again. Using this function with the z parameter
requires using P3D as a parameter for size(), as shown in the third
example above. This function can be further controlled with
pushMatrix() and popMatrix().
Examples
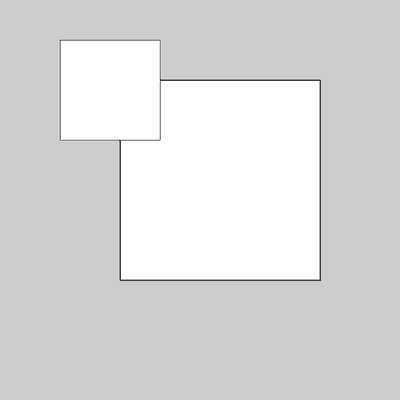
size(400, 400); rect(120, 80, 200, 200); scale(0.5); rect(120, 80, 200, 200);![Image output for example 1]()
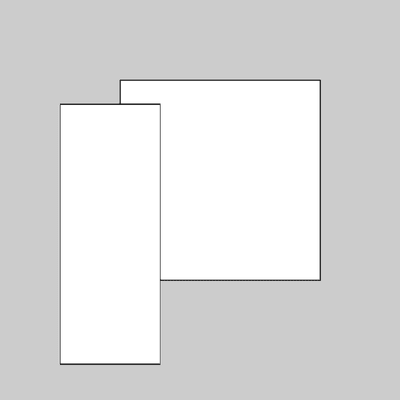
size(400, 400); rect(120, 80, 200, 200); scale(0.5, 1.3); rect(120, 80, 200, 200);![Image output for example 2]()
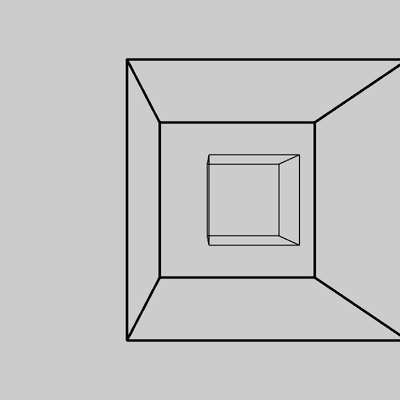
// Scaling in 3D requires P3D // as a parameter to size() size(400, 400, P3D); noFill(); translate(width/2+48, height/2); box(80, 80, 80); scale(2.5, 2.5, 2.5); box(80, 80, 80);![Image output for example 3]()
Syntax
scale(s)scale(x, y)scale(x, y, z)
Parameters
s(float)percentage to scale the objectx(float)percentage to scale the object in the x‑axisy(float)percentage to scale the object in the y‑axisz(float)percentage to scale the object in the z‑axis
Return
void

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.